Choosing the right business model is crucial for success in the competitive e-commerce landscape. This article will delve into a comprehensive comparison of two popular options: dropshipping and private label. We’ll examine the pros and cons of each, highlighting key differences in startup costs, profit margins, inventory management, branding opportunities, and overall business scalability. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which path—dropshipping or private label—best aligns with your entrepreneurial goals and resources, empowering you to make an informed decision for your e-commerce venture.
What is Dropshipping and How Does It Work?

Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where a store doesn’t keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, when a store sells a product using the dropshipping model, it purchases the item from a third party (a dropshipping supplier) and has it shipped directly to the customer. The seller never sees or handles the product.
The process is straightforward: A customer places an order on your online store. You forward that order and customer details to your dropshipping supplier. The supplier then packages and ships the order directly to the customer. Your profit is the difference between the price you charged the customer and what you paid the supplier.
Key benefits of dropshipping include low startup costs, minimal inventory management, and the ability to offer a wide variety of products. However, it also presents challenges such as lower profit margins, reliance on third-party suppliers, and potential shipping complications.
What is Private Labeling and Its Benefits?
Private labeling is a retail strategy where a company manufactures products and sells them under another company’s brand name. The company that sells the product doesn’t actually manufacture it; they purchase it from a manufacturer and then rebrand it.
Key benefits of private labeling include increased profit margins compared to dropshipping, as you’re not paying per-unit fees to a third party. You also gain more control over product quality, branding, and packaging, allowing for stronger brand building and potentially higher customer loyalty.
Further, private labeling allows for greater flexibility in product development and customization. You can create unique products tailored to your target market’s preferences, establishing a distinctive presence in the market.
However, private labeling requires a higher upfront investment compared to dropshipping due to the need to purchase inventory in bulk. There is also a greater level of risk associated with managing inventory and potential unsold stock.
Comparing Costs: Dropshipping vs Private Label
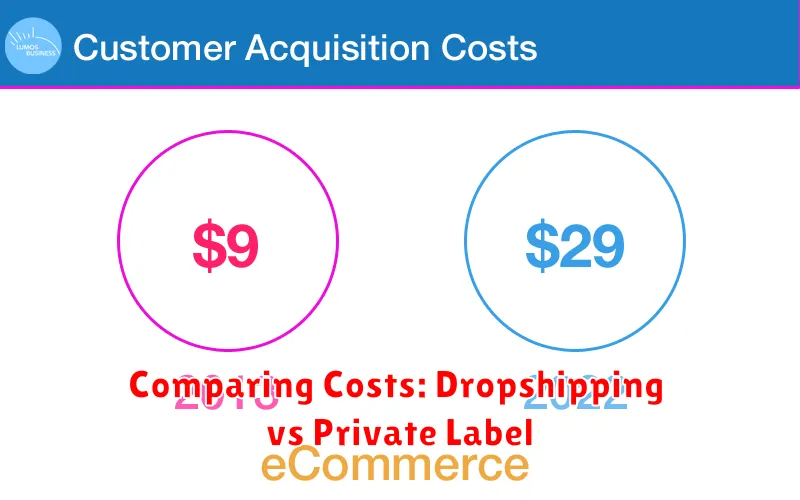
Dropshipping boasts lower initial startup costs. You avoid upfront investments in inventory and warehousing, paying only for products when orders are placed. However, profit margins are typically lower due to the supplier’s markup and potential shipping costs.
Private labeling requires a significantly larger upfront investment. This includes product sourcing, minimum order quantities (MOQs), packaging design, and inventory storage. However, it offers higher profit margins due to greater control over the pricing and branding.
Ongoing costs also differ significantly. Dropshipping involves ongoing marketing and advertising expenses, as well as potential supplier-related issues affecting order fulfillment and shipping times. Private labeling demands ongoing inventory management, potentially including storage fees and handling costs, but gives you greater control over quality and fulfillment speed.
Ultimately, the most cost-effective option depends on your budget, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. A thorough cost analysis considering both initial and ongoing expenses is crucial for making an informed decision.
The Pros and Cons of Dropshipping
Dropshipping offers several advantages. It requires low startup costs, as you don’t need to hold inventory. This also allows for a wide product range with minimal risk. Furthermore, it’s relatively easy to set up and manage, making it accessible to beginners. The scalability is another significant plus; you can expand your business quickly without substantial upfront investment.
However, dropshipping also presents certain challenges. Profit margins are often lower due to the involvement of multiple parties. Shipping times can be longer and less reliable, potentially impacting customer satisfaction. Inventory management can be complex, requiring careful tracking of stock levels across various suppliers. Furthermore, dependence on suppliers creates vulnerability to issues like product quality inconsistencies and order fulfillment delays. Finally, building brand loyalty can be more difficult compared to private label models due to lack of control over product branding and packaging.
The Pros and Cons of Private Labeling
Private labeling offers several advantages. It allows for greater brand control, enabling you to cultivate a unique identity and customer loyalty. Higher profit margins are typically achievable compared to dropshipping due to the elimination of a middleman. Furthermore, private labeling provides opportunities for stronger brand storytelling and the development of a dedicated customer base.
However, private labeling also presents some challenges. Higher upfront costs are involved, including product design, manufacturing, and inventory management. Inventory risk is significant; unsold stock can tie up capital. Building brand awareness and establishing a strong market presence requires a substantial marketing investment. Furthermore, the complexity of managing production and logistics can be demanding.
How to Choose the Right Business Model for Your Store
Choosing between dropshipping and private label depends on your resources, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. Consider these key factors:
Startup Costs: Dropshipping requires significantly lower upfront investment, as you don’t need to purchase inventory. Private labeling necessitates substantial initial investment in product development, manufacturing, and inventory.
Inventory Management: Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management, as the supplier handles it. Private labeling requires managing your own inventory, including storage, shipping, and potential losses from unsold stock.
Profit Margins: Dropshipping generally offers lower profit margins due to higher competition and lower pricing. Private labeling allows for higher profit margins due to brand ownership and control over pricing.
Branding & Control: Private labeling provides complete brand control, allowing for stronger brand building and customer loyalty. Dropshipping offers less control over branding and product quality, relying on your supplier’s capabilities.
Scalability: Both models can be scaled, but private labeling may require more significant investment to manage increased demand and inventory effectively.
Ultimately, the best business model depends on your individual circumstances. Carefully weigh the pros and cons based on your resources, risk tolerance, and aspirations for your store’s growth.
Marketing Strategies for Both Models
Dropshipping and private label businesses require distinct yet overlapping marketing approaches. For dropshipping, focusing on high-volume, low-margin sales is key. Strategies include paid advertising (PPC on platforms like Google and Facebook), influencer marketing, and leveraging social media trends to drive quick sales. A strong emphasis on retargeting existing website visitors is also crucial.
Private label businesses, conversely, often prioritize building a brand and fostering customer loyalty. Marketing efforts tend to be more long-term and focus on brand storytelling, content marketing (blog posts, high-quality product photography), email marketing, and potentially affiliate marketing. While paid advertising is still relevant, the focus shifts towards building brand awareness over immediate sales.
Both models benefit from SEO optimization to improve organic search rankings. However, the specific keywords targeted will differ based on the business model and product offerings. Analyzing competitor strategies and adapting successful tactics is also a valuable approach for both.
Scaling Your Business with the Right Model
Choosing between dropshipping and private label significantly impacts your business scaling potential. Dropshipping offers a lower barrier to entry, allowing for quicker initial scaling due to minimal upfront investment. However, profit margins are typically lower, and scaling beyond a certain point can become challenging due to reliance on third-party suppliers and less control over branding and quality.
Private labeling, conversely, demands a larger initial investment in inventory and branding. This higher upfront cost can slow initial growth. However, it fosters greater brand control, allowing for higher profit margins and easier scalability through established supply chains and consistent product quality. Building brand loyalty becomes easier, facilitating larger-scale marketing and expansion.
Ultimately, the best model depends on your risk tolerance, financial resources, and long-term goals. Dropshipping suits entrepreneurs seeking faster initial growth with limited capital, while private labeling is better suited for those willing to invest more upfront for greater control and long-term profitability.